
Published: Invalid Date
5 min read
#React
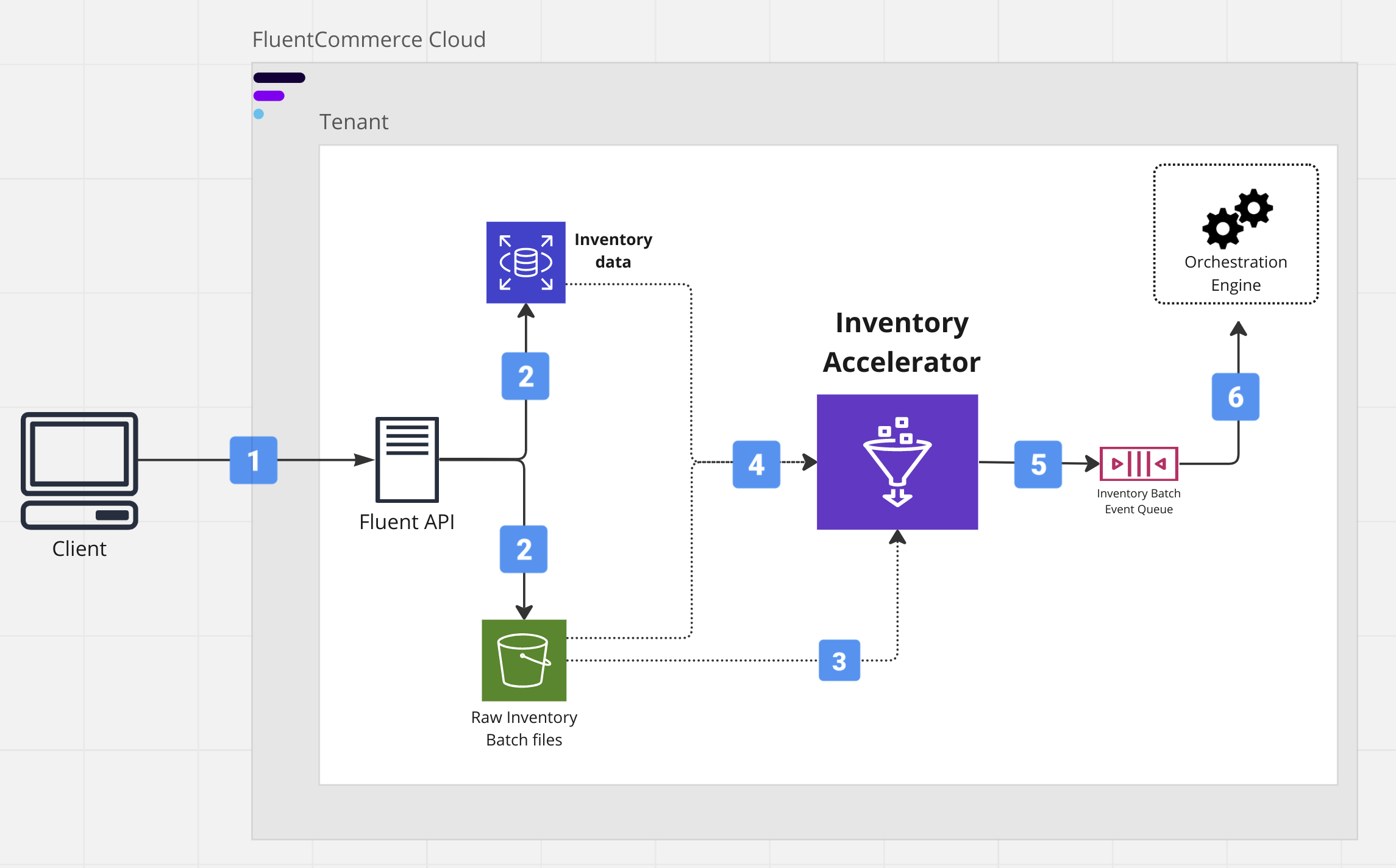
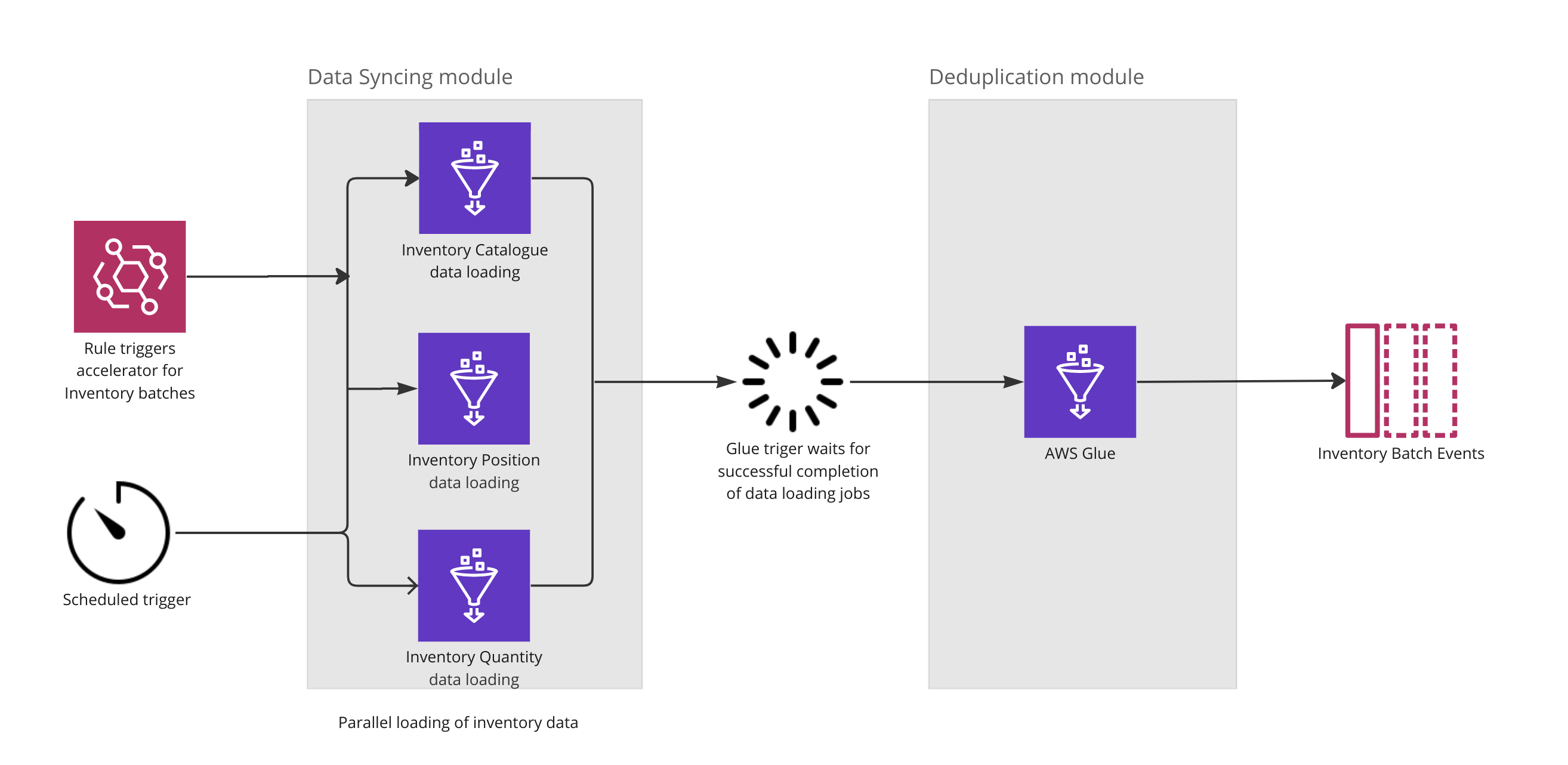 The Accelerator execution is triggered either by the arrival of new inventory batch items or by a fixed scheduler, whichever happens first. Then, the data syncing module runs multiple parallel jobs to capture the latest snapshot of inventory data in the relational database. Once the three entity snapshots are loaded, the deduplication module starts filtering out the "changed inventory data" and produces events for all such batch items.
The Accelerator execution is triggered either by the arrival of new inventory batch items or by a fixed scheduler, whichever happens first. Then, the data syncing module runs multiple parallel jobs to capture the latest snapshot of inventory data in the relational database. Once the three entity snapshots are loaded, the deduplication module starts filtering out the "changed inventory data" and produces events for all such batch items.| Scenario | E2E execution timew/o the accelerator | E2E execution timewith the accelerator | improvement |
| 99% Redundant Inventory Data | 54 minutes | 34 minutes | ��37.00% |
| 92% Redundant Inventory Data | 58 minutes | 40 minutes | ��31.00% |
| 80% Redundant Inventory Data | 80 minutes | 57 minutes | ��28.75% |
| 50% Redundant Inventory Data | 65 minutes | 57 minutes | ��12.3% |
Steve Zhang
Copyright © 2026 Fluent Commerce